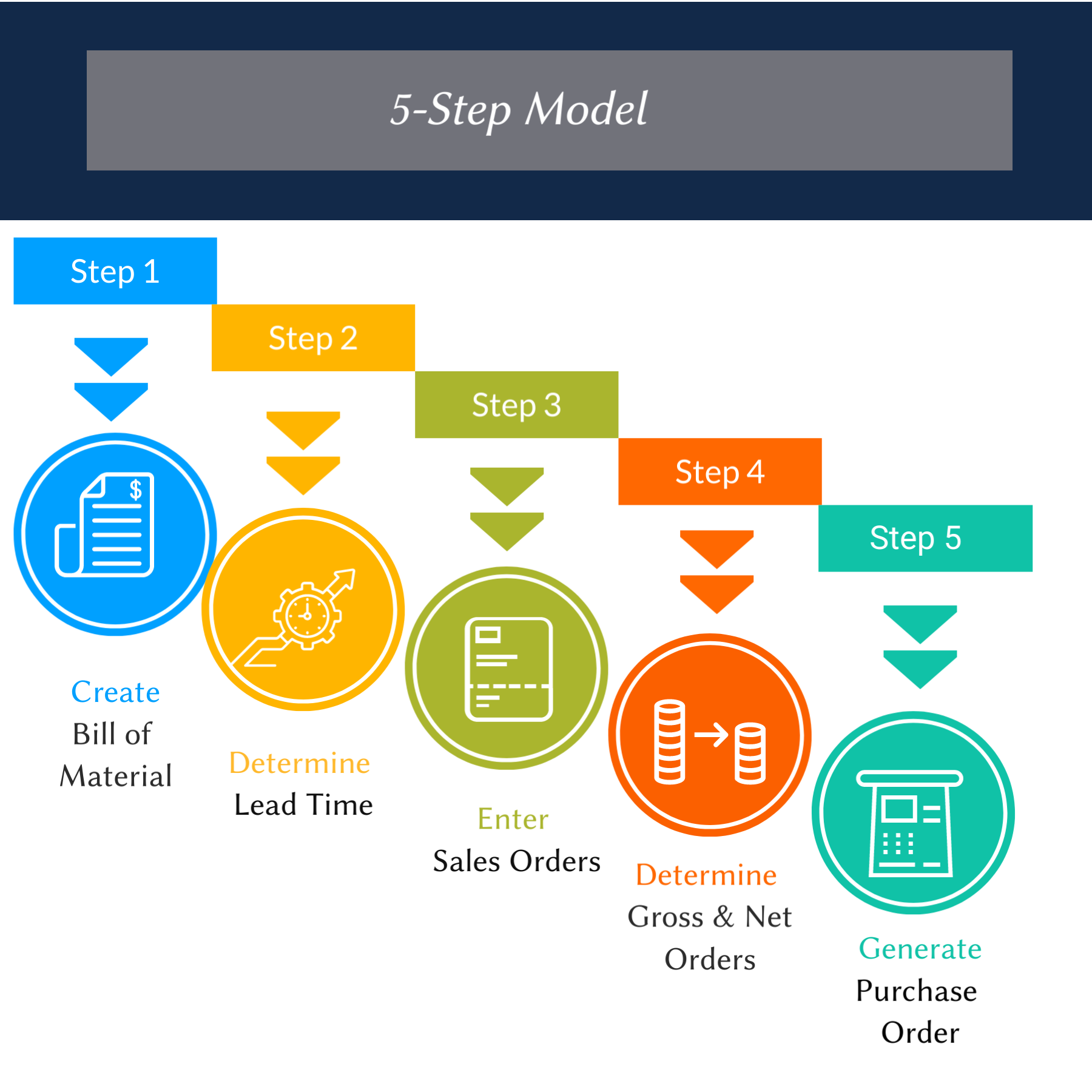
Step 1: Create the Bill of Materials (BOM)
The first step in MRP is to create a BOM for the final product. A BOM is a comprehensive list of all the raw materials required to produce one finished product. The BOM should include all components, their quantities, and specification details. Suppose a furniture manufacturer wants to create a sofa. In that case, the BOM will include the wood frame, foam cushions, fabric cover, nails, screws, and any other components necessary to construct the product.
Step 2: Determine the Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time required between ordering raw materials and receiving them. To ensure on-time production, it is necessary to estimate lead times accurately. Manufacturers should consider multiple factors, including supplier processing times, shipping, and inspections. Some lead times are standard, while others may change depending on the size of an order or supplier capacity.
Step 3: Enter Sales Orders
The next step in the MRP process is to enter sales orders for finished products. Sales orders include customer orders or forecasts of demand for finished products. By entering sales orders into the system, businesses can track demand and determine the required quantity of materials. For example, a furniture manufacturer may have a sales order for ten sofas to be delivered within a month.