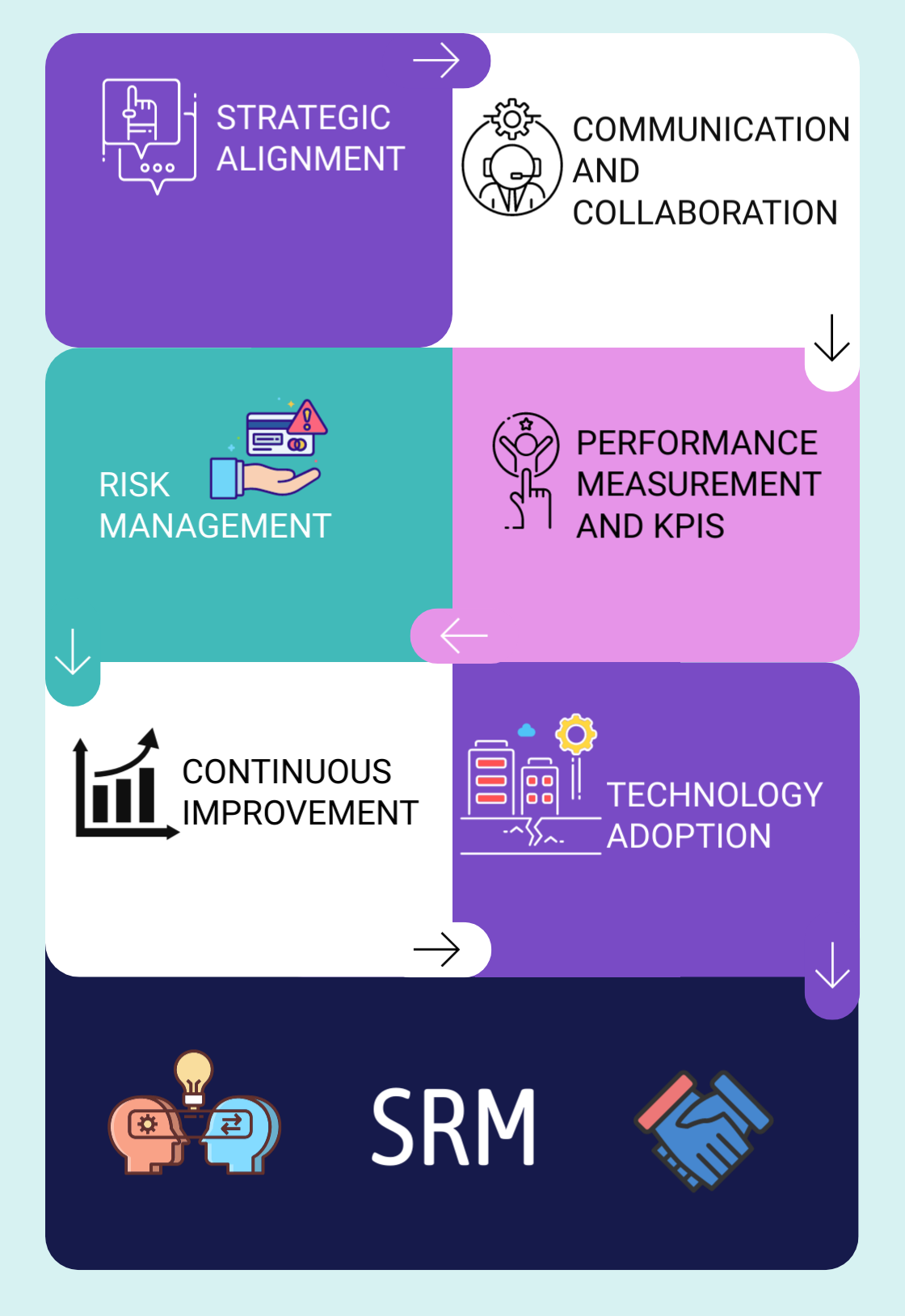
Key Components of Supplier Relationship Management
1. Strategic Alignment: Understanding Business Goals: To effectively manage supplier relationships, organizations must align supplier strategies with their own business objectives. This involves a deep understanding of the company's mission, vision, and long-term goals.
Segmentation of Suppliers: Not all suppliers are equal. Segmenting suppliers based on factors such as criticality, strategic importance, and risk allows organizations to tailor their approach to each segment.
2.Communication and Collaboration:
Open and Transparent Communication: Establishing clear lines of communication is fundamental. Regular communication helps build trust and ensures that both parties are aligned in their expectations.
Collaborative Planning: Collaborative planning involves joint efforts in forecasting, demand planning, and product development. This collaborative approach fosters innovation and efficiency.
3.Risk Management:
Identifying and Assessing Risks: Understanding and mitigating risks is crucial in supplier relationship management. This involves identifying potential risks, assessing their impact, and developing strategies to manage or mitigate them.
Contingency Planning: Organizations should have contingency plans in place to address unforeseen events such as natural disasters, geopolitical changes, or supplier disruptions.
4. Performance Measurement and KPIs:
Establishing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Defining clear KPIs allows organizations to measure supplier performance objectively. KPIs may include quality metrics, on-time delivery, and cost-effectiveness.
Regular Performance Reviews: Regular reviews provide an opportunity for constructive feedback, allowing both parties to address issues, celebrate successes, and identify areas for improvement.
5. Continuous Improvement:
Feedback Loops: Establishing feedback loops enables continuous improvement. Soliciting feedback from suppliers and providing feedback on their performance fosters a culture of continuous learning and adaptation.
Lean and Agile Practices: Embracing lean and agile practices in the supply chain allows organizations to respond quickly to changes, optimize processes, and drive continuous improvement.
6.Technology Adoption:
Implementing SRM Software: Leveraging technology, such as SRM software, can streamline processes, enhance visibility, and facilitate data-driven decision-making.
Digital Collaboration Platforms: Digital collaboration platforms enable real-time communication and document sharing, reducing lead times and enhancing overall efficiency.