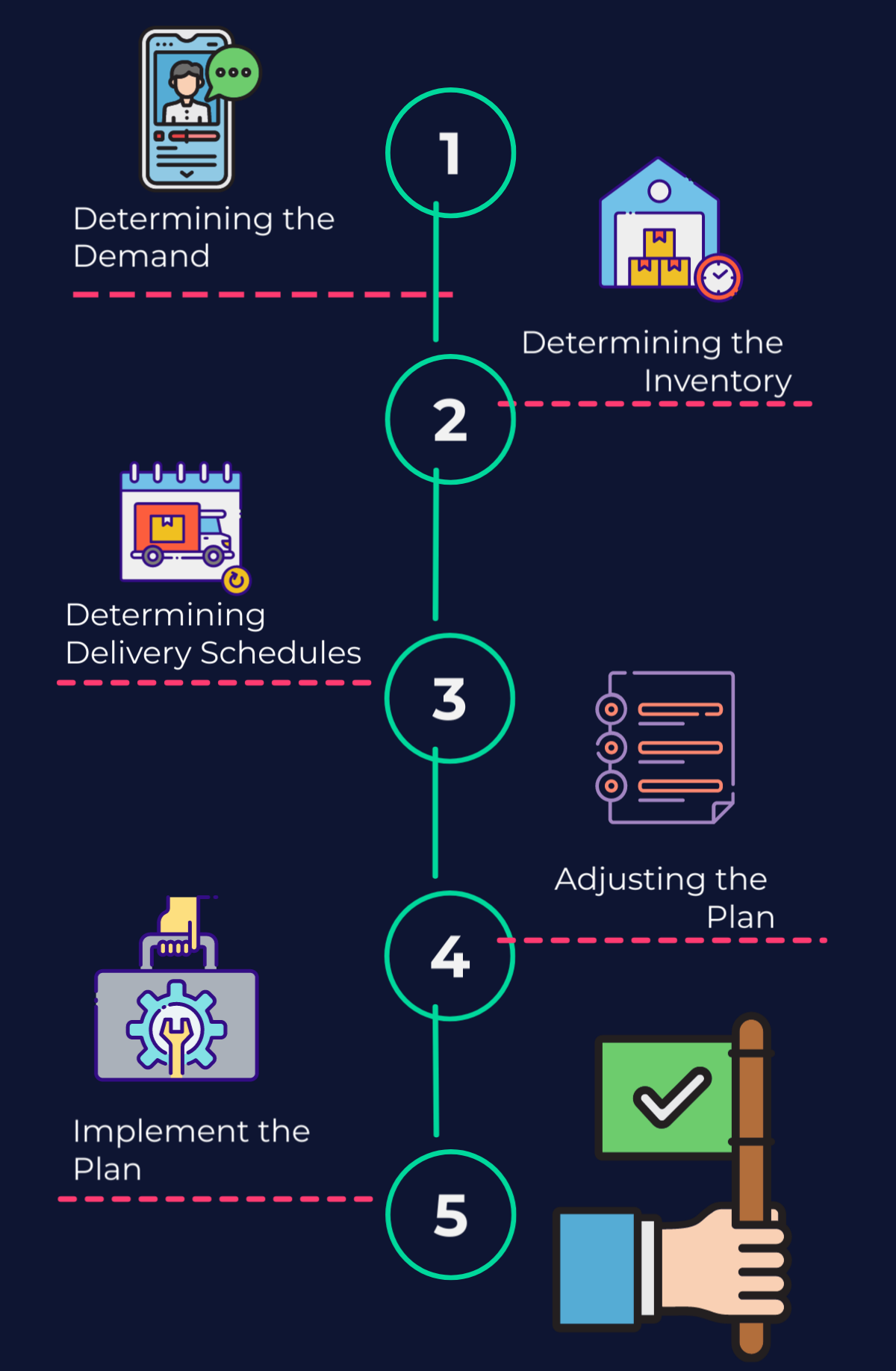

In conclusion, the Distribution Requirements Plan (DRP) is an essential tool in supply chain management. This plan helps companies ensure that inventory is available when it is needed, in the right amounts, and at the lowest possible cost. By following the step-by-step process, businesses can streamline their inventory management process and optimize their distribution requirements. Companies that implement DRPs successfully can gain significant advantages, such as increasing productivity, reduced delivery costs, better inventory management, the ability to respond to sudden challenges and opportunities, and increased customer satisfaction. For more insights and strategies on effective supply chain management, visit UpskillUtopia. Embracing DRP can lead to a more efficient and responsive supply chain, positioning companies for long-term success.
